Best Practice for workflows
The Goal is to provide coding/implementation Guidelines for iGRC.
Identifiers
Always add the project/facet identifier as prefix in the workflow definition:
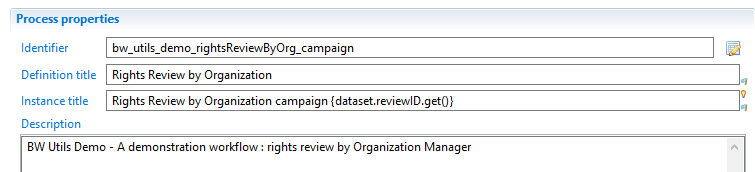
Remember to add the .get() in the instance title even if it's not done by the editor.
The instance title should be different than the definition title and be based on workflow variables so that different instances can be identified easily by users in the portal.
Localisation
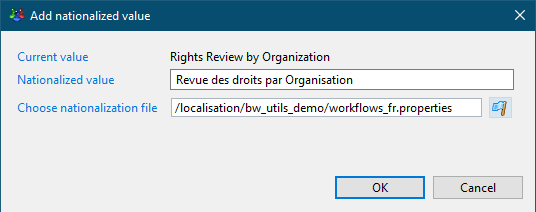
Always use the localisation files (create your own .properties files if needed):

This allows the clients to modify the workflow labels without modifying the workflow itself, and allows multiple languages.
Repeat for each language:
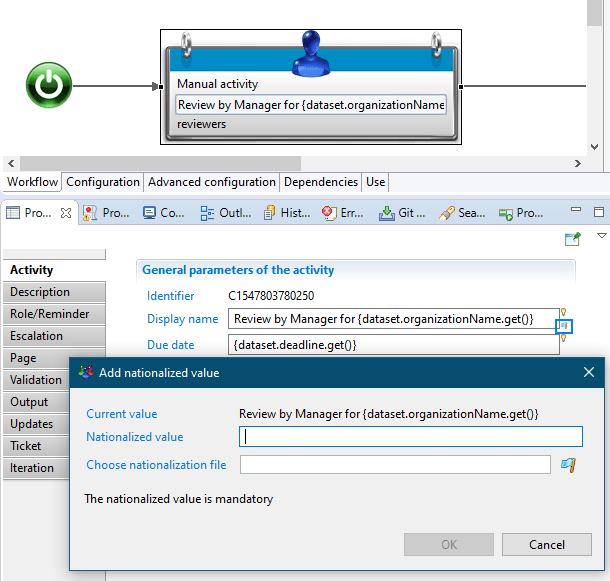
This has to be done for all the workflows Definition title and Instance title; and for all manual Tasks:
Variables
Recommendations:
- Always add a description;
- Use structures if possible;
- Use the correct type/ledger type.
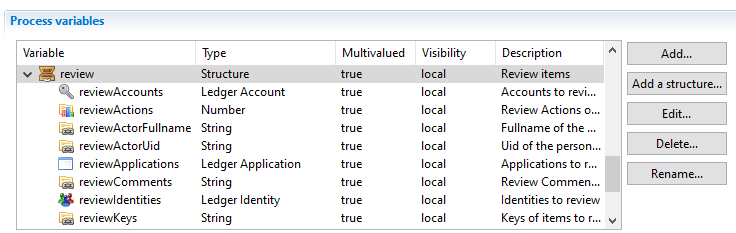
For structures, prefix the variables names with the structure name, so that they are always together (when using auto-complete in a page for instance).
Start / End
Always add the workflow identifier to the Start and End components: they have no unique identifiers like other worklfow activities (for instance C1547803780250):
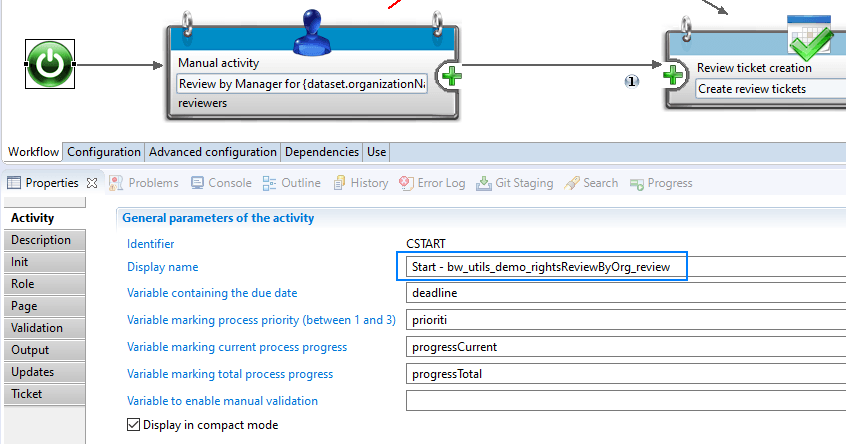
This allows for easier debug via the logs.
The same goes for route components.
Status / Progress / Information
Try to map as much information as possible so that the taskManager and other interfaces won't show empty fields:
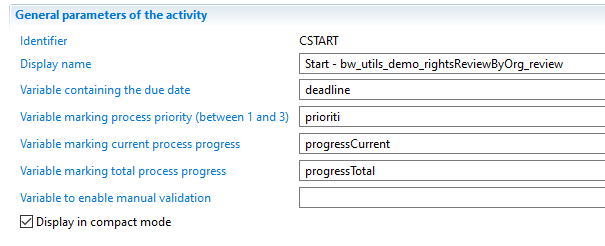
The same goes for Workflow information that you might require:
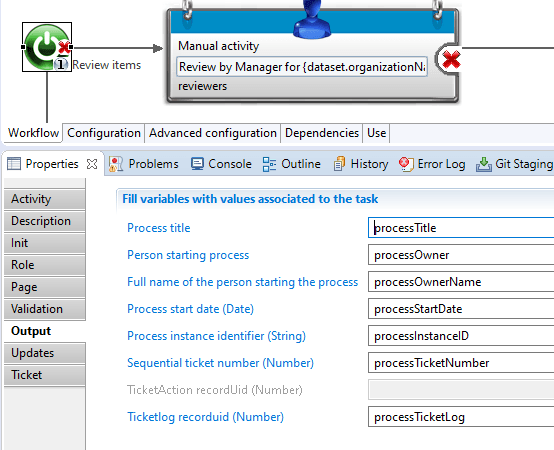
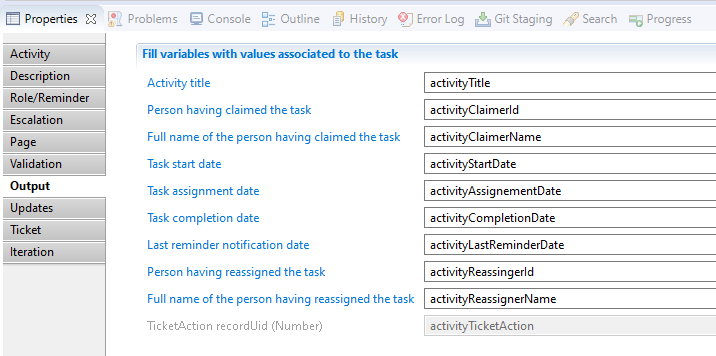
And for tasks:
Routes
Keep in mind all the use cases that might occur.
For example in a Detail process of a review:
- There is nothing to review;
- The task expires;
- The manager completes the task.
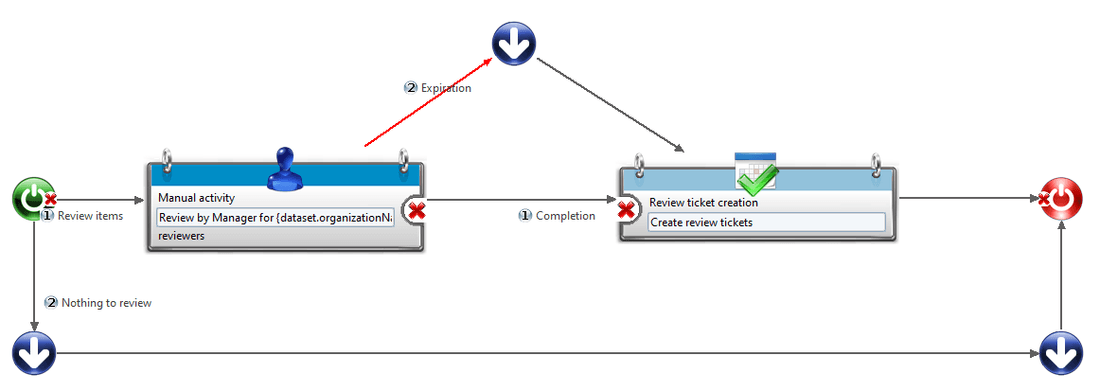
Add labels to routes so that you don't have to look at the conditions.