SAML Access
The SAML authentication allows to rely on a federated identity repository. In this case, Tomcat will delegate the authentication and the authorization mechanism to a third party (the Identity Provider).
This use case is very interesting when an Identity Provider has been deployed in the company or if the solution aims to be used from a Cloud based environment. It will literally rely on the Identity Provider for such purposes.
What's interesting here is that the Identity Provider does not need to be installed on the Tomcat server, it is another server.
When authenticating in federated mode, the protocol of choice is SAMLv2.
Here is how it works:
- The User Agent (UA) is the end user web browser
- The Service Provider (SP) is the Identity Analytics tomcat web server
- The Identity Provider (IdP) is the third party accountable for authentication and authorization
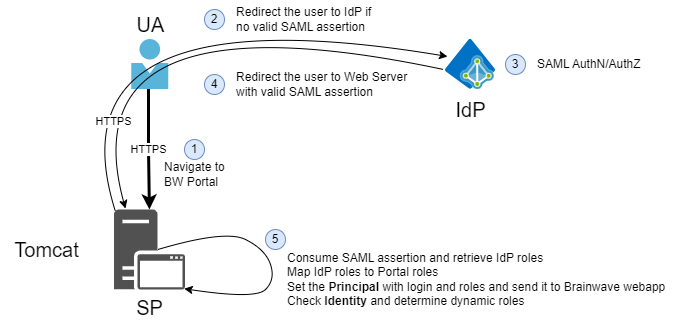
As you can see here, everything is done through the HTTP/HTTPS protocol with simple HTTP redirects and HTTP forms.
When the user attempts to connect to the service provider, it detects that the user is not authenticated, generates a challenge in SAML format and redirects the user to the identity provider with this challenge.
The identity provider analyses the challenge, authenticates the user and redirects him to the service provider with a response. The response contains all the required information regarding the user and his roles.
The SAML challenge/response mechanism involves XML, time stamping and XML digital signature (at a glance, a challenge is sent to the identity provider, a response is built by the identity provider, it contains the user identity, his roles, the initial challenge and a validity time frame. The response is digitally signed by the identity provider. The response is sent back to the service provider which verifies the digital signature, the challenge, the validity time frame and acts accordingly).
Almost all major players are now leveraging the SAMLv2 protocol to authenticate users and are acting as Identity providers (Idp):
- Microsoft ADFS
- Google G suite
- Sales force
You can also delegate authentication and authorization to best of breed solutions through the SAMLv2 protocol:
- Okta
- InWebo
- LastPass
- OneLogin
- Forgerock
- ...
Identity Analytics is providing a sample implementation of the SAMLv2 protocol for Tomcat 8/9. You will find here all the information needed to configure SAMLv2 support for authentication and authorization with a third party Idp.
This implementation is SAMLv2 compliant and should be used with any identity providers SAMLv2 compliant.
Configuration procedure
Step 1: Declare the Identity Analytics application in IdP
First step is to declare your Identity Analytics Web application in order for the IdP to recognize it and perform AuthN/AuthZ process for User Agent request coming from the application.
Identity Analytics provides some samples regarding some IdP:
The information listed above is provided as an example only. This methodology is not supported by Identity Analytics, but has been tested.
At the end, no matter the IdP solution, a XML metadata file that represents this SP configuration should be generated and provided by the IdP to be deployed in SP side (see later in this article).
Step 2: Deploy SAML configuration in Tomcat
In the following procedure, we will use below variables:
Variable | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|
| Tomcat installation root folder | /etc/tomcat9/ |
| Folder that contains Tomcat configuration files | /etc/tomcat9/conf |
| Folder that contains all libraries used by the Tomcat | /usr/share/tomcat9/lib |
| Archive that contains Identity Analytics JAVA library used to perform SAML AuthN/AuthZ | bw-tomcat-9.0-saml-libs.zip |
| Identity Analytics JAVA library used to perform LDAP AuthN/AuthZ | bw-tomcat-9.0-addons.jre8-X.jar |
| File that contains mapping between AD groups and Portal roles | rolemapping.properties |
| XML IdP configuration metadata file provided by the IdP | idp-metadata.xml |
| XML SP configuration metadata file | sp-metadata.xml |
| File that contains static roles | staticrole.properties |
| Name of the iGRC Tomcat webapp | sandbox |
| Identity Analytics Web Portal URI | /sandbox/portal |
| Identity Analytics Web Portal URL |
Prerequisites
To ensure this installation procedure, you should first download some required <SAML_BW_ARCHIVE> and <SAML_BW_LIB> Identity Analytics libraries available here depending on the Tomcat version installed:
- Tomcat 8 (tested with Tomcat 8.5.9)
bw-tomcat-8.5-saml-libs.zipbw-tomcat-8.5-addons.jre8-X.jar
- Tomcat 9 (tested with Tomcat 9.0.53)
bw-tomcat-9.0-saml-libs.zipbw-tomcat-9.0-addons.jre8-X.jar
It is also admitted that:
- Tomcat instance is installed and available
- The operator has RW privileges in needed files and folders to proceed to the installation
This sample implementation relies on OpenSAML and LastPass SAML, both provided under Apache License, Version 2.0.
Tomcat configuration
If you are under Linux, beware of files and folders rights.
First step is to deploy Identity Analytics SAML libraries, JDBC driver and Authenticators in Tomcat:
Under the <TOMCAT_LIB_FOLDER_HOME> folder.
- Add following files:
<SAML_BW_ARCHIVE> - Unzip the archive in this folder:
<SAML_BW_LIB> - Create a folder
org/apache/catalina/startup. In this folder, create aAuthenticators.propertiesfile with below content
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
BASIC=org.apache.catalina.authenticator.BasicAuthenticator
CLIENT-CERT=org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SSLAuthenticator
DIGEST=org.apache.catalina.authenticator.DigestAuthenticator
FORM=org.apache.catalina.authenticator.FormAuthenticator
NONE=org.apache.catalina.authenticator.NonLoginAuthenticator
SPNEGO=org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SpnegoAuthenticator
SAML=com.brainwave.tomcat.authenticator.saml.SAMLAuthenticator
Next step is to create and configure the SAMLAuthenticator.properties file. Under the <TOMCAT_CONF_FOLDER> folder, Create a SAMLAuthenticator.properties file with below content.
# SAML Authenticator property file
# copyright Radiant Logic
# idpMetadata: Identity Provider Metadata as an XML file located in the /conf subdirectory by default
# spMetadata: Service Provider Metadata as an XML file located in the /conf subdirectory by default
# roleMapping: contains a properties file name, located in /conf. It converts a dynamic role name provided by the Identity Provider to a local role name,
# the property file is on the form idprolename=localrolename
# defaultRoleList: Roles associated to the user by default as a comma separated string
# staticRole: contains a properties file name, located in /conf. It lists all the roles per principal, the property file si in the form login=roleList where roleList is in the form role1,role2,role3
# checkRealm: Once authenticated through SAML, do we test the 'user' against the configured Realm? (this can be useful if you want to configure user roles locally or with a third party Realm).
# Note: The test is done with the user login and a blank password.
# roleAttribute: If any, the name of the SAML response attribute which contains the list of the dynamic roles for the user (most of the time groups names)
# genericUsers: If any, the name of the roles names who will be used as user names: if the user is a member of such group, the group becomes the user name. It is used to convert single
# authentications to generic accounts where the
# account name represents a profile such as "standard user", "power user", "admin user"
# genericUserPattern: when a genericUser is found, this optional parameter can be used to format the user login. {login} and {generic} can be used and will be dynamically replaced by their
# corresponding value. For instance: {login}({generic})
# defaultURI: The URI where the user will be redirected once the authentication is done. This is used for "Idp initiated use cases" only, when dealing with "SP initiated use cases", the user is redirected
# to the initial URL in any case
# forceURI: The URI where the user will be redirected once the authentication is done in any case, except when dealing with "SP initiated use cases"
#
# To add debugging infos, please add the following line at the end of the /conf/logging.properties file:
# com.brainwave.tomcat.authenticator.saml.SAMLAuthenticator.level = ALL
idpMetadata=<SAML_IDP_METADATA_FILE>
spMetadata=<SAML_SP_METADATA_FILE>
roleMapping=<SAML_ROLE_MAPPING_FILE>
defaultRoleList=user
staticRole=<SAML_STATIC_ROLE_FILE>
checkRealm=false
roleAttribute=groups
genericUsers=user
genericUserPattern={login} ({generic})
defaultURI=<WEBAPP_URI>
forceURI=<WEBAPP_URI>
Above fields should be set accordingly to your project context. Here is a short description of those configuration attributes.
Variable | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|
| A pointer to the | idp-metadata.xml |
| A pointer to the | sp-metadata.xml |
| Contains a relative | /sandbox/portal |
| Contains a relative | /sandbox/portal |
| If set to | false |
| cCntains a list of roles who are associated to users who are successfully authenticated by the IdP. | user |
| Contains the name of the | groups |
| Property file used to dynamically map the role names provided by the IdP to local roles names. | rolemapping.properties |
| Property file is used to declare the users roles. | static-role.properties |
| Property that can substitute an individual with a generic account. | user |
| Property used to format the user login | {login} ({generic}) |
For each property, you can find more details For each property, you can find more details here.
Step 3: Identity Analytics Portal generation
From your Studio, in the Export tab of your project technical configuration:
- Select
SAML authentication

- Save your technical configuration
- Generate the
<WEBAPP_NAME>web portal using igrc_portal command line or from the Studio
Once configured, a new SAML authentication method is available.
Note: the SAML method is declared in the /WEB-INF/web.xml file under the security configuration in the auth-method parameter.
<login-config>
<auth-method>SAML</auth-method>
</login-config>
If you don't setup SAML authentication schema from technical configuration, you won't be able to authenticate via SAML.
The SAML configuration is declared in the <TOMCAT_CONF_FOLDER>/SAMLAuthenticator.properties file configured earlier.
Step 4: Deploy Identity Analytics Portal
If you are under Linux, beware of files and folders rights.
Once your <WEBAPP_NAME> webapp is generated, the last step is to:
- Deposit it under
<TOMCAT_INSTALL_FOLDER>/webappsfolder - Start the Tomcat
The Portal should be accessible from your browser using <WEBAPP_URL>/<WEBAPP_URI>.
Debug
To activate traces, add the following line at the end of the /conf/logging.properties. Do not use this in production. This is just for troubleshooting SAML request/response.
com.brainwave.tomcat.authenticator.saml.SAMLAuthenticator.level = ALL
Downloads
SAMLAuthenticator.properties
idp-metadata.xml
rolemapping.properties
sp-metadata.xml
staticroles.properties